Briefly Describe the Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation Pathways
Vernice Chun and Dale Go 3. Blood is pumped from the left ventricle of the heart through the aorta and arterial branches to the arterioles and through capillaries where it reaches an equilibrium with the.
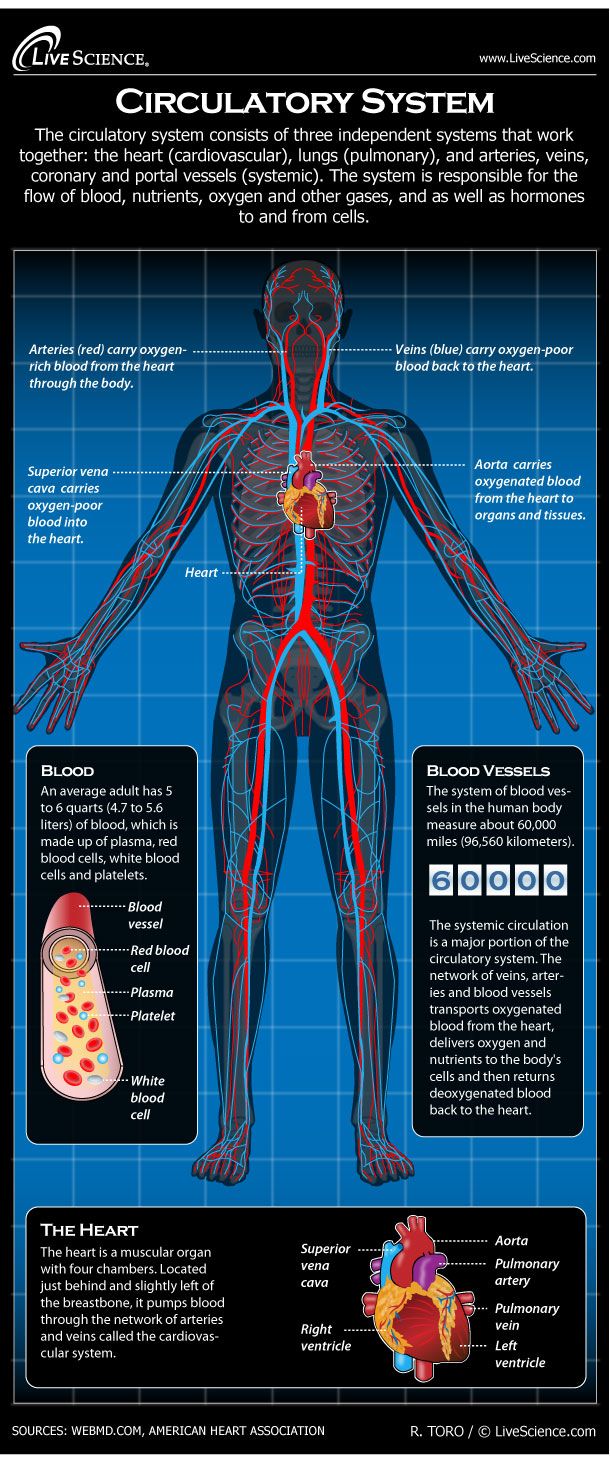
Human Circulatory System Diagram How It Works Live Science
6 rows The pulmonary and systemic circulation work harmoniously to maintain homeostasis but they do.

. Pulmonary hypertension occurs when pressure in blood vessels that lead from the heart to the lungs is too. Pulmonary circulation pathway lungs. Briefly describe the pulmonary and systemic circulation pathways.
Pulmonary Circulation and Systemic Circulation By. The capillaries form a fine network around the pulmonary vesicles grape-like air sacs at the end of the airways. Pulmonary circulation Here the blood without oxygen called as the deoxygenated blood travels from the right side of the heart to the lungs.
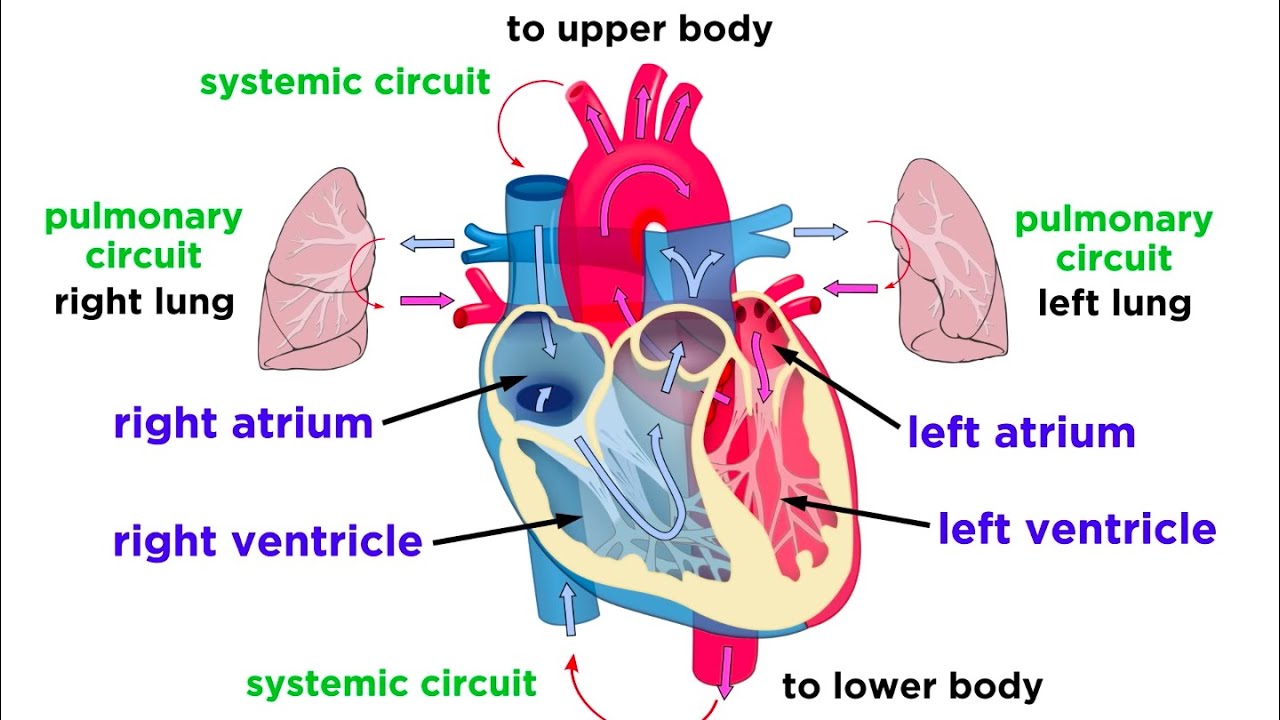
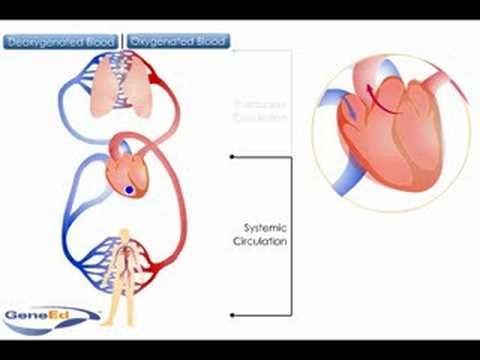
The blood moves through pulmonary circulation and then continues on through systemic circulation. Pulmonary circulation the circuit through the lungs where blood is oxygenated. The deoxygenated blood shoots down from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
Carries oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart thru the systemic arteries to al the organs and tissues. Pulmonary circulation is the system of transportation that shunts de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re-saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation. The blood moves to the lungs exchanges carbon dioxide for oxygen and returns to the left atrium.
The pulmonary system is the path blood takes through the lungs receiving fresh oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide. Describe the organization of the coronary circulation 4231. From the right atrium the blood is pumped into hearts right ventricle via the tricuspid valve.
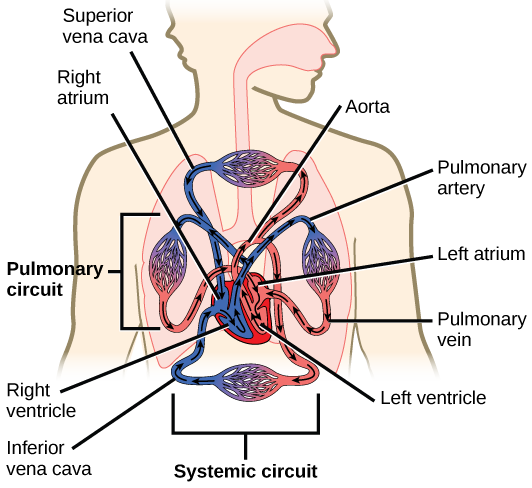
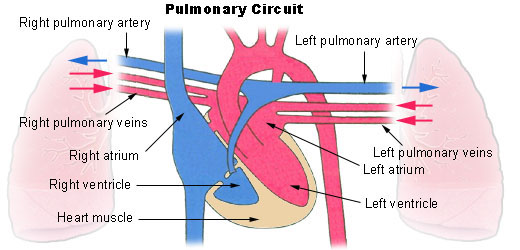
Pathway of Pulmonary Circulation From the right atrium the Deoxygenated blood is pumped through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle. The oxygenated blood shoots from the left atrium to the left ventricle below to begin. Systemic circulation in physiology the circuit of vessels supplying oxygenated blood to and returning deoxygenated blood from the tissues of the body as distinguished from the pulmonary circulation.
The right ventricle pumps low-oxygen blood into the pulmonary artery which branches off into smaller and smaller arteries and capillaries. Coronary circulation part of the systemic circulatory system that supplies blood to and provides drainage from the tissues of the heart. Deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body enters the heart from the inferior vena cava while deoxygenated blood from the upper body is delivered to the heart.
The heart then pumps it out of the right ventricle and into the pulmonary arteries to begin pulmonary circulation. Pulmonary circulation occurs only between the heart and lungs. As shown in the image above there are actually two circulatory systems in the body.
During diastole the increased aortic pressure above the valves forces blood into the coronary arteries and thence into the musculature of the heart. In the human heart two coronary arteries arise from the aorta just beyond the semilunar valves. Pulmonary and Systemic Circulations 3.
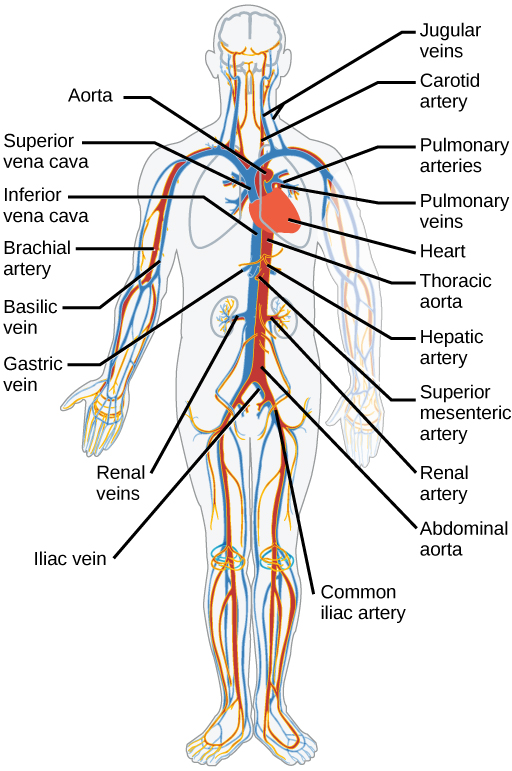
1 body 2 inferiorsuperior vena cava 3 right atrium 4 tricuspid valve 5 right ventricle 6 pulmonary arteries 7 lungs 8 pulmonary veins 9 left atrium 10 mitral or bicuspid valve 11 left ventricle 12 aortic valve 13 aorta 14 body. Pulmonary circulation Pulmonary circulation carries deoxygenated blood away from the heart to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood back to the heart. Systemic circulation carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the right atrium of the heart by the superior and inferior vena cava.
The cardiovascular system is composed of two circulatory paths. The main function of it is to carry oxygen-poor blood to the lungs where it picks up 02 expels excess CO2 and water and carries oxygen-rich blood back to. After delivering oxygen and receiving carbon dioxide in the systemic capillaries returns deoxygenated blood thru the systemic veins to the right atrium where the pulmonary circulation begins.
The blood enters the pulmonary circulation stream from the system circulation stream when the blood with depleted oxygen reserves reaches the right atrium via the inferior and superior venae cavae. Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation. Pulmonary circulation pathway quizlet.
Coronary arteries deliver oxygenated blood from the aorta to the heart. Its main function is to carry oxygen-poor blood to the lungs where gas exchange can occur and carry oxygen-rich blood back to the heart. Briefly describe the pulmonary and systemic circulation pathways.
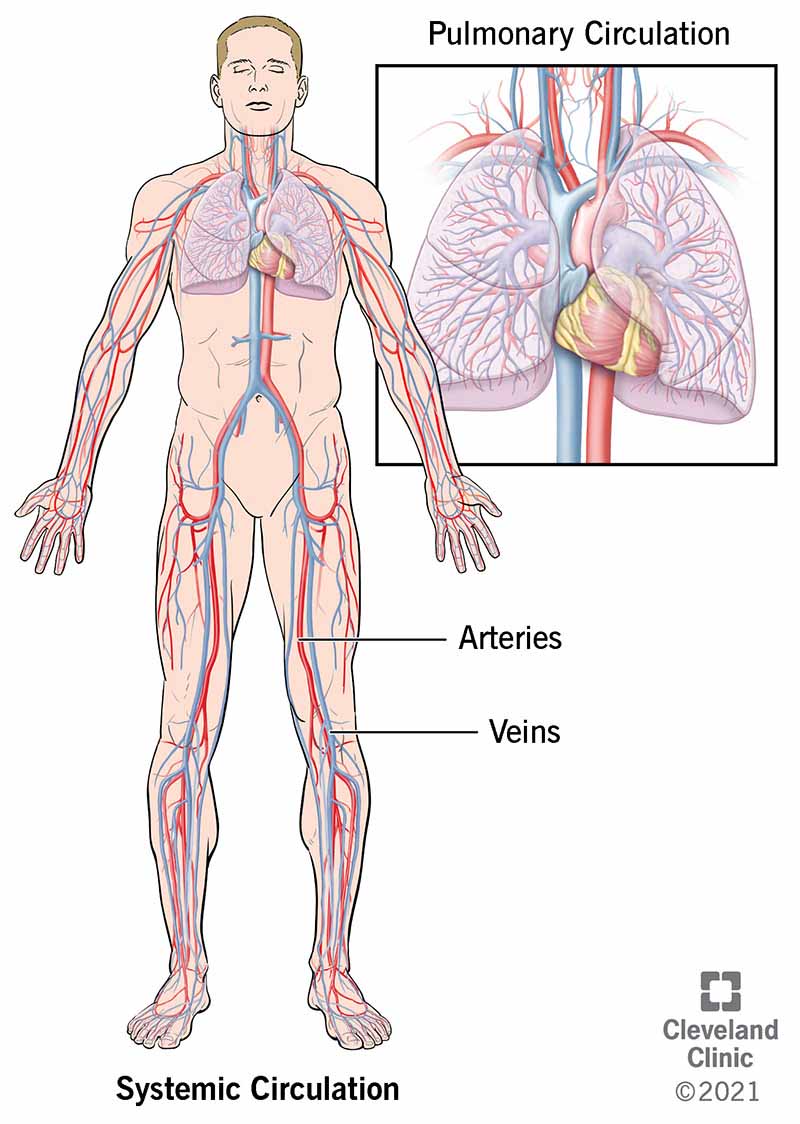
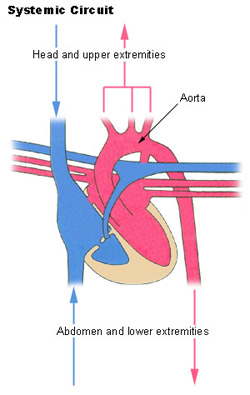
The main function of systemic circulation is to carry oxygen-rich blood to all the cells and transport oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. The systemic circulation is the portion that brings oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. The Route of Pulmonary Circulation.
The heart gets its own supply of blood through the coronary circulation. The systemic circuit is the path of circulation between the heart and the rest of the body excluding the lungs. When a heart contracts and forces blood into the blood vessels there is a certain path that the blood follows through the body.
Pulmonary circulation occurs between the heart and the lungs. The pulmonary circulation is the portion that brings blood to the lungs and back. Pulmonary circulation carries oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium of the heart by the pulmonary vein.
The systemic circulatory system provides food and nutrients to all the organs tissues and cells in the body. In humans blood travels through two types of pathways the pulmonary circulation pathway and the systemic circulation pathway. After moving through the pulmonary circuit oxygen-rich blood in the left ventricle leaves the heart via the aorta.
In the lungs exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place and the blood now becomes oxygenated. This blood is circulated from the aorta to the rest of the body by various major and minor arteries. Distinguish between the pathways followed for the pulmonary and systemic circuits in terms of oxygenation of the blood workload and its effect on the structure of the ventricular wall 423.
Pulmonary circulation pathway steps. Pulmonary circulation pathway blood. Correct pathway of pulmonary circulation.
In summary from the video in 14 steps blood flows through the heart in the following order. And systemic circulation the circuit through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. Identify the main arterial and venous components of the coronary circulation and indicate those areas of the heart which they.
Pulmonary systemic circulation 1. This is where pulmonary circulation begins.

2016 Pearson Education Inc Ppt Download
Circulatory System Anatomy And Function
The Respiratory System Youtube
How Are The Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation Described Quora
The Circulatory System Review Article Khan Academy

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulations Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Heart 3 Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation Youtube

17 2d Systemic And Pulmonary Circulation Medicine Libretexts
11 3 Circulatory And Respiratory Systems Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
The Circulatory System Review Article Khan Academy

Pulmonary And Systemic Circulations Advanced Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation

Pulmonary Circulation Definition Function Diagram Facts Britannica
Difference Between Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation Definition Circulation Pathway Importance
Difference Between Pulmonary And Systemic Circulation Definition Circulation Pathway Importance

Systemic Circulation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Circulatory System The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Systemic And Pulmonary Circulation Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment